Agriculture
- Nutrients
NutrientsPlant nutrients are the molecular compounds necessary to maintain plant life. Plants, like animals and other forms of life, require a great diversity of compounds. Molecules of these compounds are used to build and maintain cells and to perform...
- Nutrition In Agriculture
Nutrition in AgricultureExtensive research has been conducted to investigate the nutritional requirements of different crops and ways to enhance soil fertility, which has greatly benefited agricultural production. Even though people have known for more...
- Main Functions Of Plant Nutrients
Nutrient Functions Nitrogen (N) Synthesis of proteins (growth and yield). Phosphorus (P) Cellular division and formation of energetic structures. Potassium (K) Transport of sugars, stomata control, cofactor of many enzymes, reduces susceptibility...
- Hydroponic Fertilizer Solutions
Plants typically grow with their roots in soil and their stems and leaves in the air. They get some of the elements they require from the air (for example, most of the carbon and much of the oxygen used by the plant comes from the carbon dioxide taken...
- Nutrients Availability At Different Ph Value
The pH value measures the ratio of H+ ions to OH-base ions in the soil. If the soil solution has more H+, the soil is acidic. If the OH-dominates, the soil is alkaline. The equal balance between them is neutral and its value 7.0. The soil pH value interacts...
Agriculture
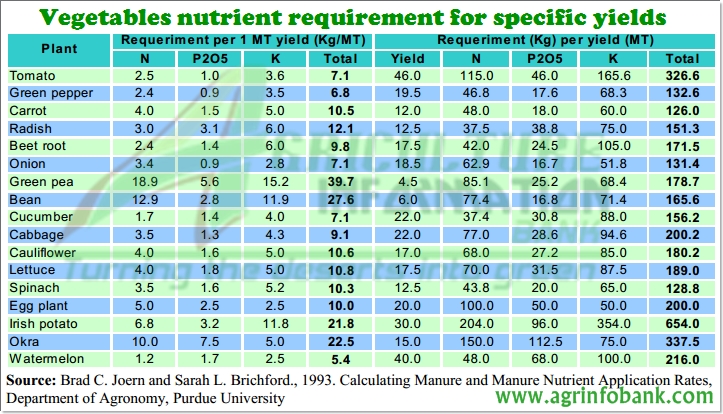
Vegetables nutrient requirement for specific yields
Plant Nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth:
- In its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or
- That the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.
This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 17 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are obtained from the soil. Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media:
- The primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K)
- The three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulphur (S), magnesium (Mg)
- The macronutrient Silicon (Si)
- The micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), selenium (Se), and sodium (Na)
- Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than its older ones. So when nutrients are mobile, the lack of nutrients is first visible on older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. When a less mobile nutrient is lacking, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays lower in the older leaves. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. This phenomenon is helpful in determining what nutrients a plant may be lacking.

- Nutrients
NutrientsPlant nutrients are the molecular compounds necessary to maintain plant life. Plants, like animals and other forms of life, require a great diversity of compounds. Molecules of these compounds are used to build and maintain cells and to perform...
- Nutrition In Agriculture
Nutrition in AgricultureExtensive research has been conducted to investigate the nutritional requirements of different crops and ways to enhance soil fertility, which has greatly benefited agricultural production. Even though people have known for more...
- Main Functions Of Plant Nutrients
Nutrient Functions Nitrogen (N) Synthesis of proteins (growth and yield). Phosphorus (P) Cellular division and formation of energetic structures. Potassium (K) Transport of sugars, stomata control, cofactor of many enzymes, reduces susceptibility...
- Hydroponic Fertilizer Solutions
Plants typically grow with their roots in soil and their stems and leaves in the air. They get some of the elements they require from the air (for example, most of the carbon and much of the oxygen used by the plant comes from the carbon dioxide taken...
- Nutrients Availability At Different Ph Value
The pH value measures the ratio of H+ ions to OH-base ions in the soil. If the soil solution has more H+, the soil is acidic. If the OH-dominates, the soil is alkaline. The equal balance between them is neutral and its value 7.0. The soil pH value interacts...
